The information on this page is historical. Food labels are changing and the term Guideline Daily Amount is being replaced by Reference Intake (RI). Read about the new nutrition labelling requirements.
Whether you are choosing between products in a supermarket, deciding what to
have for a snack at home or need a drink whilst out and about, using the check,
compare and choose approach can help you to make food choices based on your
individual needs.
The approach has three clear stages:
- Check the food label and what it contains.
- Compare foods with other similar products.
- Choose the foods that best suit your needs.
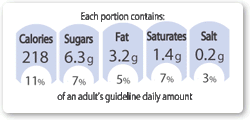
How to use the GDA label
The example of a cereal bar and yogurt show how to use the check, compare and
choose approach.
The two options are products that might typically be eaten as a snack.
If
you are watching your saturated fat intake you can use the GDA label to make
the
best choice to suit your needs.
- Check: first of all, looking at the label will show you that the cereal bar contains
one
gram of saturates (saturated fat), that’s five percent of the Guideline Daily
Amount (GDA). The yogurt
contains 2.5
grams of saturates (saturated fat), which is 13 percent of the GDA. - Compare: using this information you can see that the yogurt contains more saturated fat
than the cereal bar. The yogurt contains 1.5 grams more saturates (saturated
fat) than the cereal bar,
which
is eight percent more of the GDA. - Choose: if you are watching your saturated fat intake you might want to pick the cereal
bar, which contains less than the yogurt. Or if you do choose the yogurt,
be sure to
keep using labels in order to stay within the GDA for saturates (saturated
fat).
More product label comparisons
More examples on how to use the GDA label by applying the check, compare and
choose approach.
Last reviewed: 19 Jun 2013
Example of GDA label
Ask FDF
Working on my own recipe for an organic drink. How do I go about getting the information for the labels?
Today's poll
FSA’s salt campaign uses GDA figures

Did you know?
GDAs were developed in the late 1990s by a group of experts based on COMA
medical report – see GDAs explained for more.
Consumer insight
84% of shoppers use GDA labels to pick a product with low nutrient score before
purchase.[6]
